TUGAS 2 PBO C
Setelah menjalani pertemuan ke-2 kelas PBO, saya akan mencoba menjelaskan cara untuk membuat suatu contoh biodata dengan bahasa java dan juga menjelaskan Bab 8.1 - 8.6 yang ada pada buku Deitel.
Contoh Biodata
Cara untuk membuat contoh biodata adalah dengan menggunakan langkah-langkah berikut :
- Buatlah class baru dengan menekan "New Class" dan diberi nama Biodata
- Double click class yang telah dibuat untuk mengeditnya
- Gantilah source codenya dengan source code berikut
- Compile code tersebut
- Click kanan pada class yang telah dibuat, kemudian pilih "new Biodata()" dan beri nama sesuai nama mahasiswanya
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 | /** * Class Biodata menampung data mahasiswa, nama, alamat, umur, jurusan * * @author Avind Pramana Azhari * @version 0.2 8 Oktober 2020 */ public class Biodata { public Biodata(){ System.out.println("Data Mahasiswa "); System.out.println("========================="); System.out.println("Nama Mahasiswa : Toni Kurniadi"); System.out.println("Alamat Mahasiswa : Jl. Sukarno 50 Malang"); System.out.println("Umur Mahasiswa : 20 tahun"); System.out.println("Jurusan Mahasiswa : Informatika"); System.out.println("Jurusan Mahasiswa : Informatika"); System.out.println("Nomor HP : 088888888888"); } } |
Demikian untuk pembuatan contoh biodata.
Materi Bab 8.1 - 8.6
Bab 8.1 Introduction
Subbab ini berisi pengenalan tentang pendalaman pada pembuatan class, mengkontrol akses ke member sebuah class dan membuat constructors.
Bab 8.2 Time Class Case Study
contoh pertama merupakan 2 class berbeda yaitu Time1 dan Time1Test yang harus dideklarasikan di file yang berbeda, karena dua-duanya merupakan public class.
Pendeklarasian class Time1 adalah sebagai berikut
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 | // Time1 class declaration maintains the time in 24-hour format. public class Time1 { private int hour; // 0 - 23 private int minute; // 0 - 59 private int second; // 0 - 59 // set a new time value using universal time; throw an // exception if the hour, minute or second is invalid public void setTime( int h, int m, int s ) { // validate hour, minute and second if ( ( h >= 0 && h < 24 ) && ( m >= 0 && m < 60 ) && ( s >= 0 && s < 60 ) ) { hour = h; minute = m; second = s; } // end if else throw new IllegalArgumentException("hour, minute and/or second was out of range" ); }// end method setTime // convert to String in universal-time format (HH:MM:SS) public String toUniversalString() { return String.format( "%02d:%02d:%02d", hour, minute, second ); } // end method toUniversalString // convert to String in standard-time format (H:MM:SS AM or PM) public String toString() { return String.format( "%d:%02d:%02d %s", ( ( hour == 0 || hour == 12 ) ? 12 : hour % 12 ), minute, second, ( hour < 12 ? "AM" : "PM" ) ); } // end method toString }// end class Time1 |
Pada contoh ini, class Time1 tidak mendeklarasikan constructor, jadi class tersebut mempunyai default constructor yang diberikan compiler. Setiap instansi int akan diberikan nilai 0.
Throwing exception
Pada line 14, code akan mengecek apabila argument h,m, dan s ada didalam jangkauan 0-23 untuk j. 0-59 untuk m, dan 0-59 untuk d. Apabila ada di luar jangakauan, SetTime melakukan throws an exeption dengan tipe IllegalArgumentException pada line 21 yang memberi tau client code bahwa adanya argument yang tidak valid. Statement throw berguna untuk membuat object baru, dalam contoh ini bernama IllegalArgumentException. Tanda kurung setelahnya berfungsi untuk memanggil constructor IllegalArgumentException dan juga dapat menampilkan error message. Setelah object exception dibuat, throw statement langsung memberhentikan method setTime dan exception dikembalikan ke kode menset time.
Method toUniversalString
Isinnya berupa cara untuk menampilkan waktu menjadi bentuk HH:MM:SS dengan format 24 jam. Perbedaan cara menampilkan dengan menggunakan System.out.print adalah, cara menampilkannya dengan format string,
Method toString
Isinya yaitu cara menampilkan waktu dengan bentuk HH:MM:SS AM/PM dengan format 12 jam.
Using Class Time1
Deklarasikan Time1, sebagai contoh :
Time1 sunset; // sunset can hold a reference to a Time1 object
Selanjutnya untuk membuat class Time1Test
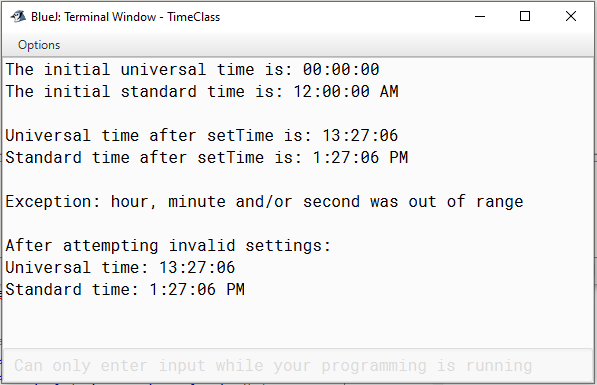
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 | public class Time1Test { public static void main( String[] args ) { // create and initialize a Time1 object Time1 time = new Time1(); // invokes Time1 constructor // output string representations of the time System.out.print( "The initial universal time is: " ); System.out.println(time.toUniversalString()); System.out.print( "The initial standard time is: " ); System.out.println( time.toString() ); System.out.println(); // output a blank line // change time and output updated time time.setTime( 13, 27, 6 ); System.out.print( "Universal time after setTime is: " ); System.out.println( time.toUniversalString() ); System.out.print( "Standard time after setTime is: " ); System.out.println( time.toString() ); System.out.println(); // output a blank line // attempt to set time with invalid values try { time.setTime( 99, 99, 99 );// all values out of range } // end try catch ( IllegalArgumentException e ) { System.out.printf( "Exception: %s\n\n", e.getMessage() ); } // end catch // display time after attempt to set invalid values System.out.println( "After attempting invalid settings:" ); System.out.print( "Universal time: " ); System.out.println( time.toUniversalString() ); System.out.print( "Standard time: " ); System.out.println( time.toString() ); } // end main }//end class Time1Test |
Setelah dijalankan, output dari Time1Test adalah sebagai berikut :
Dikarenakan argument yang dipakai adalah 99,99, dan 99, maka, program akan menangkap IllegalArgumentException yang ada pada line 28 dan menampilkan pesan error. Setelah itu, waktu ditampilkan lagi untuk memastikan waktu tidak diubah dengan input baru yang tidak valid.
8.3 Controlling Access to Members
Pada subbab ini, menjelaskan akses public dan private. Akses public artinya dapat dipanggil siapa saja, sedangkan private hanya bisa dipanggil di dalam class itu sendiri.
8.4 Referring to the Current Object’s Members with the this Reference
Ketika non-static method dipanggil untuk suatu object, badan method tersebut menggunakan kata kunci "this" untuk mengacu variable dan method dari object tersebut. Sebagai contoh, perhatikan source code berikut
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 | public class ThisTest { public static void main( String[] args ) { SimpleTime time = new SimpleTime( 15, 30, 19 ); System.out.println( time.buildString() ); } // end main } // end class ThisTest // class SimpleTime demonstrates the "this" reference class SimpleTime { private int hour; // 0-23 private int minute; // 0-59 private int second; // 0-59 // if the constructor uses parameter names identical to // instance variable names the "this" reference is // required to distinguish between the names public SimpleTime( int hour, int minute, int second ) { this.hour = hour; // set "this" object's hour this.minute = minute; // set "this" object's minute this.second = second; // set "this" object's second } // end SimpleTime constructor // use explicit and implicit "this" to call toUniversalString public String buildString() { return String.format( "%24s: %s\n%24s: %s", "this.toUniversalString()", this.toUniversalString(), "toUniversalString()", toUniversalString()); } // end method buildString // convert to String in universal-time format (HH:MM:SS) public String toUniversalString() { // "this" is not required here to access instance variables, // because method does not have local variables with same // names as instance variables return String.format( "%02d:%02d:%02d", this.hour, this.minute, this.second); } // end method toUniversalString } // end class SimpleTime |
outputnya adalah :
Dapat dilihat pada line 31 dan 32 menghasilkan output yang sama, ini dikarenakan method toUniversalString hanya saya yang dipakai di dalam code tersebut.Hal yang sama berlau pada variable.
8.5 Time Class Case Study: Overloaded Constructors
Perhatikan source code berikut
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 | public class Time2 { private int hour; // 0 - 23 private int minute; // 0 - 59 private int second; // 0 - 59 // Time2 no-argument constructor: // initializes each instance variable to zero public Time2() { this( 0, 0, 0 ); // invoke Time2 constructor with three arguments } // end Time2 no-argument constructor // Time2 constructor: hour supplied, minute and second defaulted to 0 public Time2( int h ) { this( h, 0, 0 ); // invoke Time2 constructor with three arguments } // end Time2 one-argument constructor // Time2 constructor: hour and minute supplied, second defaulted to 0 public Time2( int h, int m ) { this( h, m, 0 ); // invoke Time2 constructor with three arguments } // end Time2 two-argument constructor // Time2 constructor: hour, minute and second supplied public Time2( int h, int m, int s ) { setTime( h, m, s ); // invoke setTime to validate time } // end Time2 three-argument constructor // Time2 constructor: another Time2 object supplied public Time2( Time2 time ) { // invoke Time2 three-argument constructor this( time.getHour(), time.getMinute(), time.getSecond() ); } // end Time2 constructor with a Time2 object argument // Set Methods // set a new time value using universal time; // validate the data public void setTime( int h, int m, int s ) { setHour( h ); // set the hour setMinute( m ); // set the minute setSecond( s ); // set the second } // end method setTime // validate and set hour public void setHour( int h ) { if ( h >= 0 && h < 24 ) hour = h; else throw new IllegalArgumentException( "hour must be 0-23" ); } // end method setHour // validate and set minute public void setMinute( int m ) { if ( m >= 0 && m < 60 ) minute = m; else throw new IllegalArgumentException( "minute must be 0-59" ); } // end method setMinute // validate and set second public void setSecond( int s ) { if ( s >= 0 && s < 60 ) second = ( ( s >= 0 && s < 60 ) ? s : 0 ); else throw new IllegalArgumentException( "second must be 0-59" ); }// end method setSecond // Get Methods // get hour value public int getHour() { return hour; } // end method getHour // get minute value public int getMinute() { return minute; } // end method getMinute // get second value public int getSecond() { return second; } // end method getSecond // convert to String in universal-time format (HH:MM:SS) public String toUniversalString() { return String.format( "%02d:%02d:%02d", getHour(), getMinute(), getSecond() ); } // end method toUniversalString // convert to String in standard-time format (H:MM:SS AM or PM) public String toString() { return String.format( "%d:%02d:%02d %s", ( (getHour() == 0 || getHour() == 12) ? 12 : getHour() % 12 ), getMinute(), getSecond(), ( getHour() < 12 ? "AM" : "PM" ) ); } // end method toString } // end class Time2 |
Pada line 9-30 terdapat contstructor yang berfungsi memanggil method itu sendiri dengan mengisi parameter yang tidak disediakan dengan 0. Setelah itu, waktu yang sudah dimodifikasi berdasarkan masukan akan ditampilkan. Pemanggilan class Time2 ini akan dilakukan dengan class Time2Test yang mempunyai source code sebagai berikut
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 | public class Time2Test { public static void main( String[] args ) { Time2 t1 = new Time2(); // 00:00:00 Time2 t2 = new Time2( 2 ); // 02:00:00 Time2 t3 = new Time2( 21, 34 ); // 21:34:00 Time2 t4 = new Time2( 12, 25, 42 ); // 12:25:42 Time2 t5 = new Time2( t4 ); // 12:25:42 System.out.println( "Constructed with:" ); System.out.println( "t1: all arguments defaulted" ); System.out.printf( " %s\n", t1.toUniversalString() ); System.out.printf( " %s\n", t1.toString() ); System.out.println( "t2: hour specified; minute and second defaulted" ); System.out.printf( " %s\n", t2.toUniversalString() ); System.out.printf( " %s\n", t2.toString() ); System.out.println( "t3: hour and minute specified; second defaulted" ); System.out.printf( " %s\n", t3.toUniversalString() ); System.out.printf( " %s\n", t3.toString() ); System.out.println( "t4: hour, minute and second specified" ); System.out.printf( " %s\n", t4.toUniversalString() ); System.out.printf( " %s\n", t4.toString() ); System.out.println( "t5: Time2 object t4 specified" ); System.out.printf( " %s\n", t5.toUniversalString() ); System.out.printf( " %s\n", t5.toString() ); // attempt to initialize t6 with invalid values try { Time2 t6 = new Time2( 27, 74, 99 ); // invalid values } // end try catch ( IllegalArgumentException e ) { System.out.printf( "\nException while initializing t6: %s\n", e.getMessage() ); } // end catch } // end main } //end class Time2Test |
hasil outputnya adalah sebagai berikut
JIka di dalam class tidak ada constructor, maka class tersebut akan membuat default constructor. Default constructor akan menginisialisasikan hal yang dideklarasikan dengan class tersebut dengan nilai default(yaitu 0 untuk numeric, false untuk bool, dan null jika direferensikan).
Jika ada construcor di dalam class, maka diperlukan no-argument constructor jika ingin menginisialisasi ke default.




Comments
Post a Comment